 |
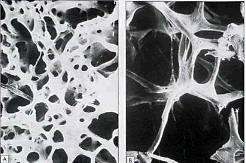
| Normal bone density- left, Osteoporosis bone density- right |
There are a number of factors that can affect bone health
- calcium deficiency- diminishes bone density, increases risk of fractures
- physical activity- inactive people have an increased risk of osteoporosis
- certain medications- prednisone, SSRIs, anti-seizure medications
- alcohol and tobacco use- alcohol can interfere with the body's ability to absorb calcium
In CF, these bone diseases can happen at any age and as you get older, the risk increases.
The malabsorption caused by CF affects the amount of vitamins and mineral the body is able to absorb. Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin and is vital to bone health in addition to calcium. It is important to take the correct amount of enzymes and maintain a nutritious diet to ensure healthy bones.
Bone Density Scan- the most common and accurate way uses a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA) scan. DXA uses low-dose x-rays. (a chest x-ray has more radiation)
2 types of DXA
- Central DXA- lie on a soft table and the scanner passes over your lower spine and hip. This scan is the best test to predict your risk of fractures.
- Peripheral DXA (p-DXA)- The smaller machines measure the bone density of smaller bones like wrists, fingers, legs.
 |
| Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Calcium |
a few foods high in calcium *values are approximate and vary based off of flavor, freshness, serving size, etc
- 1 c whole milk 290 mg
- 1/2 c almonds 190 mg
- 1 c spinach 240 mg
- 6 oz calcium fortified orange juice 261 mg
- 3 oz canned salmon 181 mg
- 1 c plain yogurt 415 mg
*It is important that you discuss any changes in your vitamin regimen, dosage, and frequency with your doctor and/or dietitian. Blood work ordered by your physician and help determine whether or not you are deficient in vitamins.

No comments:
Post a Comment